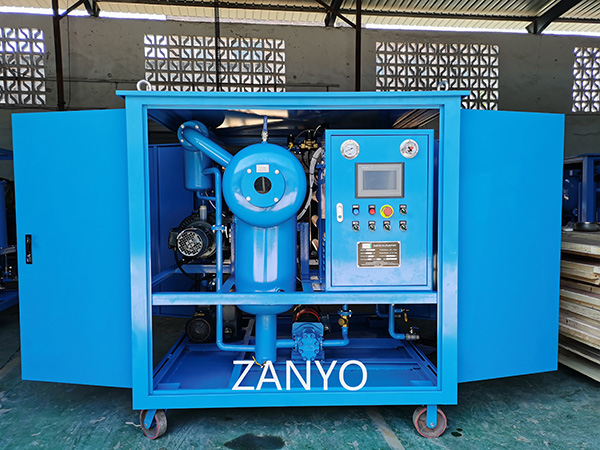
By removing impurities and contaminants, the used cooking oil is refined into a clean, high-quality product that can be converted into biodiesel. This process not only reduces waste but also helps create a renewable energy source, contributing to a greener future. In this article, we’ll explore how the purification of used cooking oil plays a key role in biodiesel production.

BUY OIL PURIFICATION MACHINE HERE
Why Recycling Used Cooking Oil Matters
Environmental Impact
Recycling used cooking oil offers significant environmental benefits. Improper disposal of this oil often leads to clogged drains and polluted water systems. When poured down sinks or drains, it can harm aquatic ecosystems and disrupt water treatment processes.
Recycling prevents these issues by ensuring proper disposal. It also reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills, where decomposing oil can release harmful greenhouse gases. By reusing this resource, communities can promote sustainability and protect the environment from unnecessary harm.
Role in Renewable Energy
Used cooking oil serves as a valuable feedstock for renewable energy production. Biodiesel, a cleaner alternative to traditional fossil fuels, is derived from this recycled oil. Unlike petroleum-based fuels, biodiesel burns more cleanly and emits fewer pollutants.
Recycling cooking oil for biodiesel production reduces dependence on non-renewable energy sources. This process supports global efforts to transition to greener energy solutions. It also highlights the potential of waste materials to contribute to energy sustainability.
Economic Benefits
Recycling used cooking oil creates economic opportunities. Businesses involved in cooking oil recycling benefit from collecting, purifying, and converting the oil into biodiesel. This industry generates jobs in collection, transportation, and processing.
Additionally, biodiesel production reduces the need for imported fossil fuels, which strengthens local economies. Restaurants and households can also save money by participating in recycling programs, avoiding fines for improper disposal. Overall, recycling used cooking oil contributes to both environmental and economic progress.
How to Achieve Purification of Used Cooking Oil
Collection and Storage
The purification process begins with collecting used cooking oil from various sources, such as restaurants, households, and food processing facilities. Proper collection ensures that the oil is not contaminated further. Once collected, the oil is transported to processing facilities for storage.
Storage plays a crucial role in maintaining the oil’s condition before purification. Facilities store the oil in large tanks designed to keep it at a stable temperature. This step prevents solidification and makes the oil easier to handle during the next stages.
Filtration
Filtration is an essential steps in removing impurities from used cooking oil. Filtration involves passing the oil through fine mesh screens to remove solid particles, such as food debris. An advanced purification system typically begins with an initial filtration step, which removes larger impurities from the used oil.
At the final stage of the purification process, more refined filtration process to eliminate smaller contaminants, ensuring the oil is of high quality. The advanced system helps achieve a cleaner, more efficient oil ready for reuse or conversion into biodiesel.
Centrifugal Separation
Centrifugal separation utilizes high-speed spinning to separate contaminants based on their density. When used cooking oil is placed in a centrifuge, the force pushes heavier particles (like food residue) to the bottom, while the cleaner oil remains on top. This method is highly efficient and works well for removing both solid and liquid contaminants, such as water.
Vacuum Distillation
Vacuum distillation is a process that uses heat and reduced pressure to separate impurities from oil. The oil is heated under vacuum conditions, causing contaminants to evaporate at lower temperatures.
This process helps remove moisture, free fatty acids, and volatile compounds without degrading the oil. It is especially useful for refining oil for biodiesel production, ensuring high-quality, purified oil.

BUY OIL PURIFICATION MACHINE HERE
Conversion of Used Cooking Oil into Biodiesel
The Transesterification Process
The transesterification process is the core method for converting purified used cooking oil into biodiesel. This chemical reaction involves mixing the oil with an alcohol, such as methanol, and a catalyst, typically sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide. The catalyst speeds up the reaction, breaking down the oil molecules into fatty acid methyl esters (FAME), which form biodiesel, and glycerin, a byproduct.
The process begins by heating the purified oil to a specific temperature to ensure optimal reaction conditions. The alcohol and catalyst mixture is then added to the heated oil. Stirring the mixture thoroughly ensures that the reaction occurs evenly.
After a set period, the mixture separates into two layers. The top layer contains biodiesel, while the bottom layer holds glycerin. The biodiesel is then extracted and washed to remove any remaining impurities or traces of alcohol and catalyst.
Quality Testing and Certification
Quality testing ensures that the biodiesel produced meets industry standards. Testing begins by analyzing the biodiesel’s chemical composition to confirm it contains the correct proportions of fatty acid methyl esters. This step ensures the fuel will perform efficiently in engines. Tests also check for impurities, such as water, glycerin, or unreacted alcohol, which can affect the fuel’s quality and safety.
Certification follows successful testing. Regulatory bodies evaluate the biodiesel to ensure it complies with environmental and performance standards. Certified biodiesel guarantees reliability and safety for consumers. It also builds trust in biodiesel as a sustainable alternative to traditional fuels.
By prioritizing quality testing and certification, biodiesel producers ensure their product meets the demands of both the market and environmental regulations. This step is crucial in the conversion process, as it validates the fuel’s readiness for widespread use.
Applications of Biodiesel
Recycled biodiesel from used cooling oil is a versatile, eco-friendly fuel with many applications. It helps reduce waste while powering different industries. Let’s look at some of its key uses.
1. Vehicle Fuel
Recycled biodiesel can be used in diesel engines, making it a great alternative to regular diesel. It helps vehicles run smoothly while producing fewer emissions. Using this fuel can save money and reduce your carbon footprint.
2. Industrial Heating
Factories, warehouses, and other industries need heating. Recycled biodiesel works as an affordable, clean heating oil replacement. It burns efficiently and reduces the release of harmful chemicals into the air.
3. Power Generation
In areas with limited access to the grid, recycled biodiesel can be used to power generators. It provides a reliable, renewable energy source for backup power or off-grid locations. It’s an excellent way to keep things running without harming the environment.
4. Agricultural Equipment
Farm machinery like tractors can use recycled biodiesel, making it a perfect fit for the agriculture industry. It’s cost-effective and helps reduce the environmental impact of traditional fuels. Farmers benefit from savings while supporting a greener future.
5. Lubrication
Biodiesel also works as a biodegradable lubricant for machinery. It’s an eco-friendly choice compared to petroleum-based oils. By using recycled biodiesel, companies can reduce waste and improve machine performance while helping the planet.
Conclusion
Recycling used cooking oil plays a crucial role in creating biodiesel, a renewable and eco-friendly fuel. This process transforms waste into a valuable resource, reducing environmental harm and supporting sustainable practices. Encouraging widespread participation in recycling practices can promote sustainability and pave the way for a greener future.